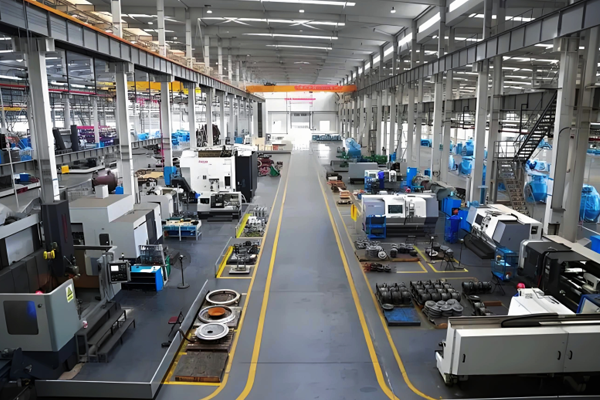
Alloy Elbow
Alloy elbow is a pipe fitting made of alloy steel, mainly used to change the direction of pipelines. Due to the high strength, high temperature resistance, high pressure resistance, and corrosion resistance endowed by alloy materials, it is indispensable in industrial pipeline systems under extreme working conditions. Here is a detailed introduction:
1、 Core feature: Performance advantages of alloy materials
The base material of alloy elbows is steel with chromium, molybdenum, nickel, vanadium, titanium and other alloy elements added to carbon steel. By adjusting the alloy composition ratio, it has comprehensive properties far beyond ordinary carbon steel:
High temperature resistance: It can work stably for a long time in high temperature environments above 400 ℃ (such as steam pipelines), and some alloys (such as Cr5Mo) can withstand temperatures above 600 ℃.
High pressure resistance: High tensile strength and yield strength, capable of withstanding high pressures above 10MPa, suitable for high-pressure fluid transportation.
Corrosion and oxidation resistance: Alloy elements form a dense oxide film (such as the passivation effect of chromium), which has a certain resistance to acidic, alkaline, or sulfur-containing media.
Creep resistance: It is not easy to undergo slow deformation (creep) due to long-term stress under high temperature and high pressure, ensuring the sealing of the pipeline.
2、 Classification of commonly used alloy materials
The performance of alloy elbows depends on the specific alloy composition, and common materials in industry include:
Chromium molybdenum alloy (Cr Mo steel)
Typical grades: 12Cr1MoV, Cr5Mo (T5), Cr9Mo (T9).
Characteristics: Outstanding high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance, suitable for steam pipelines in thermal power plants and high-temperature reaction devices in petrochemicals.
Chromium nickel alloy (austenitic alloy)
Typical grades: 304H, 316H (austenitic stainless steel containing a small amount of alloying elements, also classified as alloys).
Features: Balancing high temperature stability and corrosion resistance, suitable for high temperature corrosive environments (such as chemical cracking furnace pipelines).
Low alloy high-strength steel
Typical grades: Q345R (16MnR), 15CrMo.
Characteristics: High strength and toughness at medium and low temperatures, lower cost than high alloys, suitable for medium and high pressure water, oil and gas transportation pipelines.
Special alloys (such as nickel based alloys)
Typical grades: Inconel 600, Hastelloy C-276.
Characteristics: Preferred for extreme high temperatures (above 800 ℃) and strong corrosive environments (such as strong acids and seawater), used in high-end fields such as aerospace and nuclear industry.
3、 Manufacturing process
The forming process of alloy elbows needs to be selected based on material characteristics, especially plasticity at high temperatures. Common methods include:
Hot pressing process
Suitable for medium and low alloy materials, small and medium-sized elbows (DN15-DN500), the pipe blank is pushed into shape in the mold by heating, ensuring uniform wall thickness and high dimensional accuracy.
Hot pressing process
For high alloy, thick walled, or large-diameter elbows, the heated alloy tube blank is placed into a mold for compression molding, which can withstand greater pressure, but the heating temperature needs to be controlled to prevent alloy element burnout.
Forging process
For alloy elbows with small diameters and high pressure ratings (such as DN15-DN100), forging is used to improve material density and mechanical properties, making them suitable for ultra-high pressure systems.
4、 Classification and specifications
Divided by angle
Commonly used angles are 90 °, 45 °, and 180 °, and special angles (such as 30 ° and 60 °) can be customized to meet the requirements of complex pipeline routing.
Divided by curvature radius
Long radius (LR, R=1.5D): Low fluid resistance, suitable for most high-pressure pipelines;
Short radius (SR, R=1.0D): saves space and is used for compact layout of equipment pipelines.
Connection method
Welding connection (most common): Strong sealing after welding with pipelines, suitable for high-pressure systems;
Socket welding or threaded connection: used in small-diameter low-pressure scenarios, but alloy materials are less commonly used (higher cost).
5、 Application Fields
The performance of alloy elbows makes them a "must-have" for extreme working condition pipeline systems, mainly used for:
Power industry: Main steam pipelines and reheat steam pipelines for thermal/nuclear power plants (required to withstand high temperatures and ultra-high pressures above 540 ℃).
Petrochemical industry: High temperature and high pressure reaction pipelines for hydrocracking units and synthetic ammonia units, transporting sulfur-containing and hydrogen containing media.
Coal chemical industry: High temperature gas pipelines at the outlet of coal gasification furnaces (resistant to coal ash wear and high temperature corrosion).
Metallurgical industry: high-pressure water descaling pipelines and high-temperature flue gas pipelines for steelmaking and steel rolling systems.
Aerospace: engine cooling pipelines, hydraulic systems (requiring lightweight and extreme environmental tolerance).
6、 Execution standards
The production of alloy elbows must comply with strict standards to ensure consistency in size and performance:
International standards: ASME B16.9 (American standard butt welded pipe fittings), EN 10253-2 (European standard alloy pipe fittings).
Domestic standards: GB/T 12459 (Steel butt welded seamless fittings), DL/T 695 (High temperature and high pressure fittings for power industry), SH/T 3408 (Petrochemical fittings).
7、 Selection and maintenance points
Selection key
Match materials based on medium temperature (e.g. Cr Mo alloy is preferred if it exceeds 500 ℃), pressure (thick walled forged elbows are preferred for high pressure), and corrosiveness (low chromium alloys are avoided for sulfur-containing media).
For example, 12Cr1MoV elbows are commonly used for steam pipelines of 300MW thermal power units, and Cr5Mo elbows are used for high-pressure pipelines of hydrogenation units.
Maintenance precautions
Before installation, it is necessary to check whether there are cracks or oxide scales on the surface of the elbow (high-temperature alloys are prone to oxidation), and the inner wall should be smooth and free of impurities.
When welding, matching alloy welding rods (such as R317 welding rods for 12Cr1MoV welding) should be used, and post weld heat treatment (stress relief) should be carried out.
After long-term use, it is necessary to regularly check the wall thickness (to prevent corrosion or erosion thinning) and metallographic structure (to avoid material aging at high temperatures).
Alloy elbows solve the performance shortcomings of ordinary carbon steel in high temperature, high pressure, and corrosive environments through precise alloy ratio and process control. They are the "hard core" components that ensure safe and efficient operation in industrial pipeline systems, and their quality directly affects the reliability of the entire device.

+86-15533769121
Jango

jango@yuntaopiping.com

Beixiaozhuangzi Industrial Zone, Mengcun Hui Autonomous County
Copyright © 2025-2026 http://www.yuntaopiping.com. All Rights Reserved Yuntao Piping Group.,Ltd.Copyright