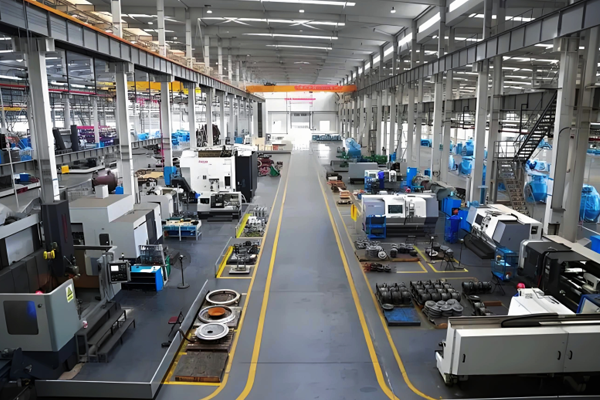
Carbon Steel Tee
Carbon Steel Tee is a T-shaped pipe fitting mainly made of carbon steel, used in pipeline systems to achieve medium diversion (one pipe divided into two pipes) or merging (two pipes combined into one). Due to its low cost, high strength, and strong adaptability, it is one of the most commonly used branch fittings in industrial and civil pipelines. Here is a detailed introduction:
1、 Core characteristics and material classification
The core advantage of carbon steel tees lies in their high cost-effectiveness (compared to stainless steel and alloy materials) and balanced mechanical properties (moderate tensile strength and toughness), making them suitable for most non corrosive media scenarios. Its materials are mainly divided into:
Ordinary carbon steel: such as Q235 and A105, with low carbon content (≤ 0.25%), good plasticity, easy processing, suitable for medium and low pressure (≤ 6.4MPa), normal temperature conditions (such as municipal water supply and drainage, low-pressure air pipelines).
High quality carbon steel: such as 20 # and 20G, with higher purity (less sulfur and phosphorus impurities), better strength and temperature resistance, suitable for medium high pressure (6.4-16MPa) and medium temperature (≤ 450 ℃) systems (such as steam pipelines and oil transportation).
Low alloy carbon steel: such as 16Mn (containing manganese alloy), with higher strength than ordinary carbon steel, can be used for high-pressure (≥ 10MPa) or low-temperature (-40 ℃ to room temperature) working conditions (such as natural gas long-distance pipelines and chemical high-pressure pipelines).
2、 Structural types and classifications
Carbon steel tees can be divided into two main types based on port diameter and angle:
1. Divided by port diameter
Straight Carbon Steel Tee: Three ports with the same diameter (such as DN100 × DN100 × DN100), used for branching of equal diameter pipelines (such as dividing the main pipeline DN200 into two DN200 branch pipes), with uniform distribution of medium flow, suitable for conventional diversion scenarios (such as tap water and compressed air pipelines).
Reducing Carbon Steel Tee: The diameter of the branch pipe is smaller than that of the main pipe (such as DN200 × DN200 × DN150), and it is used to divert the main pipe to a smaller diameter branch pipe (such as a branch pipe from DN300 to DN100), which can reduce the resistance caused by sudden changes in pipe diameter (such as municipal heating pipe branches).
2. Divided by the angle of the branch pipe
90 ° Carbon Steel Tee: The branch pipe is perpendicular to the main pipe, with a symmetrical structure and easy installation. It is suitable for most conventional branches (such as horizontal branches from building drainage risers and right angle branches for cable protection pipes).
45 ° Carbon Steel Tee: The branch and main pipes are inclined at a 45 ° angle, which can reduce the turbulence and resistance of the medium at the branch, reduce the erosion of the pipeline (such as high-speed oil and gas pipelines, reduce energy consumption and wear).
3、 Forming process: seamless vs welding
The production process of carbon steel tees directly affects their strength and applicable scenarios, mainly divided into two categories:
1. Seamless carbon steel tee
Process: Using the entire seamless carbon steel pipe as raw material, it is formed by hot pressing (heated to 800-1000 ℃ and pressed out with a mold as a branch pipe) or cold pressing (pressed by a hydraulic press at room temperature, suitable for thin-walled pipe fittings) without welding seams.
Advantages: The overall structure is dense, with excellent compressive and impact resistance, and no risk of welding defects.
Applicable scenarios: high pressure (≥ 10MPa), high temperature (≥ 300 ℃), and vibration conditions (such as power plant steam pipelines and high-pressure oil and gas transportation systems).
2. Welding carbon steel tees
Process: Cut carbon steel plates into main and branch pipe blanks, and weld them together to form a "T" shape (the main pipe is two sections of steel pipe welded, and the branch pipe is vertically welded to the side of the main pipe).
Advantages: Low production cost, customizable large caliber (such as DN1000 or above), suitable for mass production.
Limitations: The strength of the weld seam is slightly lower than that of the base metal, and post weld heat treatment is required to relieve stress.
Applicable scenarios: medium and low pressure (≤ 6.4MPa), normal temperature conditions (such as municipal water supply and drainage, low-pressure gas pipelines, ventilation pipelines).
4、 Application Fields
Carbon steel tees are widely used in the following scenarios due to their low material cost and strong performance adaptability:
Municipal engineering: Branches of tap water, sewage, and rainwater pipelines (such as DN500 main water pipes branching into two DN500 branch lines through equal diameter tees, covering different neighborhoods);
Energy industry: Branches of crude oil and natural gas transmission pipelines (such as oil pipelines leading to pump stations through reducing tees);
Industrial systems: Material transportation in chemical plants (such as branches of low-pressure solvent pipelines), branches of boiler steam pipelines (such as main steam pipes leading to branch cylinders);
In the field of architecture: heating pipes (such as vertical pipes connected to radiator branch pipes on each floor through tees), fire pipes (main pipes branching off to sprinkler branch pipes).

+86-15533769121
Jango

jango@yuntaopiping.com

Beixiaozhuangzi Industrial Zone, Mengcun Hui Autonomous County
Copyright © 2025-2026 http://www.yuntaopiping.com. All Rights Reserved Yuntao Piping Group.,Ltd.Copyright