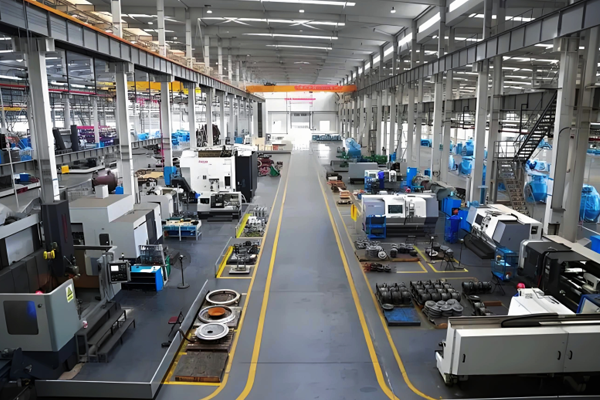
Straight Tee
Straight Tee (equal diameter tee) is one of the most commonly used branch fittings in pipeline systems. Its three interfaces have identical nominal diameters and are mainly used to evenly distribute the medium from the main pipeline to two branch pipes, or to merge the medium from two branch pipes into the main pipeline. Due to its symmetrical structure and convenient installation, it is widely used in various industrial, municipal, and civil pipeline systems. Here is a detailed introduction:
1、 Core Structure and Function
The structural characteristics of equal diameter tees are that the three ports have the same diameter (such as DN100 × DN100 × DN100) and are distributed in a "T" shape:
The two opposite ports are the main pipe (Run), used to connect the straight part of the main pipeline;
The side port perpendicular to the main pipe is called a branch, used to connect branch pipelines.
Its core function is to achieve "one pipe divided into two pipes" or "two pipes combined into one flow" without changing the diameter of the pipeline, and to ensure that the flow distribution of the medium at the branch is relatively balanced (compared to reducing the flow velocity difference caused by pipe diameter changes).
2、 Classification: By Structure and Forming Process
Divided by branch pipe angle
90 ° Straight Tee: The branch pipe is perpendicular to the main pipe at a 90 ° angle and is the most common type, suitable for most conventional branching scenarios (such as two symmetrical branch pipes leading out of the main water pipeline or branch connections of cable protection pipes).
45 ° Straight Tee: The branch pipe and main pipe are inclined at a 45 ° angle, mainly used to reduce the resistance and turbulence of the medium at the branch, suitable for high flow velocity and high viscosity media (such as oil and gas), and can reduce the erosion and wear of the pipeline (such as branches of oil and gas transmission pipelines).
Divided by molding process
Seamless equal diameter tee: formed by hot pressing, cold pressing or forging of integral pipes, without welds, with dense material and high strength, suitable for high pressure (≥ 10MPa), high temperature and corrosive working conditions (such as chemical pipelines, power plant steam systems).
Welding equal diameter tee: It is formed by cutting steel plates and welding them together (connecting the main and branch pipes), with lower cost, but slightly lower strength at the weld joint, suitable for medium and low pressure (≤ 6.4MPa) and normal temperature conditions (such as municipal water supply and drainage, low-pressure air pipelines).
Forged equal diameter tee: produced through forging process (heating and forging), it has excellent mechanical properties and high dimensional accuracy. It is mostly used for high-pressure small-diameter pipelines (such as instrument pipelines and hydraulic systems), with a diameter usually ≤ DN50.
3、 Key parameters and materials
Parameters
Nominal diameter (DN): Three ports with the same diameter, such as DN50 and DN200, are labeled in the format of "DN × DN × DN" (such as DN150 × 150 × 150);
Wall thickness grade: matched with the wall thickness of the pipeline, such as Sch40, Sch80 (American standard) or PN16, PN25 (national standard), and thick wall grade should be selected for high-pressure systems;
Angle tolerance: The perpendicularity (or inclination angle) of the branch pipe and the main pipe must comply with the standard (such as ± 1 °) to ensure alignment of the pipeline during installation and avoid stress concentration.
Common materials
Carbon steel: such as Q235, 20 #, suitable for non corrosive media such as water, steam, oil, etc., with low cost, it is the mainstream choice for industry and municipal use;
Stainless steel: such as 304 (resistant to general corrosion), 316 (resistant to acid, alkali, and seawater corrosion), used in clean or corrosive environments such as chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries;
Alloy steel: such as 12Cr1MoV (high temperature resistance), Cr5Mo (hydrogen corrosion resistance), suitable for high temperature and high pressure systems such as power plant boilers and refining units;
Plastic: such as PVC and PE, used for low-pressure and room temperature civil pipelines (such as household water supply and sewage pipe branches).
4、 Production process flow (taking seamless hot pressing forming as an example)
Preparation of billets: Select seamless steel pipes that match the diameter of the tee as billets, and calculate the length and wall thickness of the billets based on their dimensions.
Heating and punching: Heat the billet to 800-1000 ℃ (carbon steel) to soften it, and punch the hole position of the branch pipe (preliminary formed branch pipe interface) on the side of the billet through a special mold.
Expanding and Forming: Use a hydraulic press or mold to expand the hole position of the branch pipe, and adjust the size of both ends of the main pipe to ensure that the diameters of the three ports are consistent and meet the tolerance requirements.
Heat treatment: After forming, annealing treatment is carried out to eliminate internal stress generated during processing and avoid cracking during use (especially for alloy materials).
Machining: perform groove machining (for welding connections) or thread machining (for threaded connections) on three interfaces to ensure the connection accuracy with the pipeline.
Inspection: including dimensional testing (diameter, wall thickness, angle), non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic testing for internal defects), hydrostatic testing (to verify pressure resistance), etc.
5、 Application Fields
Equal diameter tees are suitable for scenarios that require "equal diameter branching" due to the consistent diameters of the three ports. Typical applications include:
Municipal engineering: In urban water pipelines, the main pipeline (DN300) is divided into two DN300 branch lines through equal diameter tees, supplying water to different areas respectively; In the sewage pipeline, two branch lines converge into the main pipeline.
Industrial pipeline: In chemical plants, the main material pipeline is divided into two reaction vessels of the same specifications through equal diameter tees; In compressed air pipelines, the main pipeline branches into two equal diameter branch pipes, each connecting different equipment.
Energy industry: In natural gas transmission pipelines, the main pipeline branches to two equally flowing user ends through equal diameter tees; In the cooling water system of the power station, the main water pipe is divided into two equal diameter branch pipes, which are respectively connected to the cooling equipment.
Civil buildings: In residential water supply systems, vertical pipes are branched into horizontal pipes on each floor through equal diameter tees; In the air conditioning refrigerant pipeline, the main pipeline branches into two equal diameter branch pipes, connecting the indoor unit.

+86-15533769121
Jango

jango@yuntaopiping.com

Beixiaozhuangzi Industrial Zone, Mengcun Hui Autonomous County
Copyright © 2025-2026 http://www.yuntaopiping.com. All Rights Reserved Yuntao Piping Group.,Ltd.Copyright